|
Voltage drop
In the cases in which the conductors of the circuit runs through long distances, the voltage drop must be calculated in fact, if the voltage drop is too large, the section of the conductor of the circuit must be increased to maintain the current between the points. The calculations for a single-phase circuit and a phase differ slightly.
Single-phase calculating voltage drop: Voltage drop [V] = 2 * Cable length * Resistance factor * Current Three-phase voltage drop calculation: Voltage drop [V] = (2 * Cable length * Resistance factor * Current) * 0.866 and in both cases: Voltage drop percentage [%] = (Voltage drop / Voltage) * 100
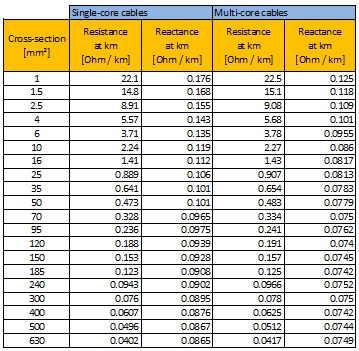
The Resistance factor depends on whether you are in AC or DC: In DC: Resistance factor = R / 1000 In AC: Resistance factor = Sqrt ( R² + X² ) / 1000 where: R = the resistance of the line per km at a temperature of 80° C X= the reactance of the line per km at a temperature of 80° C
These values are tabulated as a function of the type and section of the cable:
|